Efficient blood pumping in Bionic heart via distributed control as Multi-agent system
Published:
About
decentralised control of heart muscles dynamics to allow efficient coordination for pumping blood
Responsiblities
Programming directed acyclic graph based reinforcement learning environment with vertices representing agents, and edges equal to blood flow
Two sub-problems to solve: 1. Calculate blood flow using mathematics of fluid dynamics and then using Ford-Fulkerson max flow algorithm to derive find max blood flow in graph at any time. 2. Reinforcement learning algo to solve for optimal coordination policy
Final output will compare the pumping flow achieved at equilibrium and power efficiency of each agent. Benchmarking reinforcement learning and multi-agent approaches against hard coded baseline.
Approaches to implement the environment:
- Blender integration
- Pros
- Every accurate fluid simulation
- GUI to build things
- Cons
- Results were not that great.
- Blender python API is inflexible.
- Good for accurate single agent simulation but framing as multi-agent system is hard.
- Pros
- Matrix representation
- Graph representation - Final approach
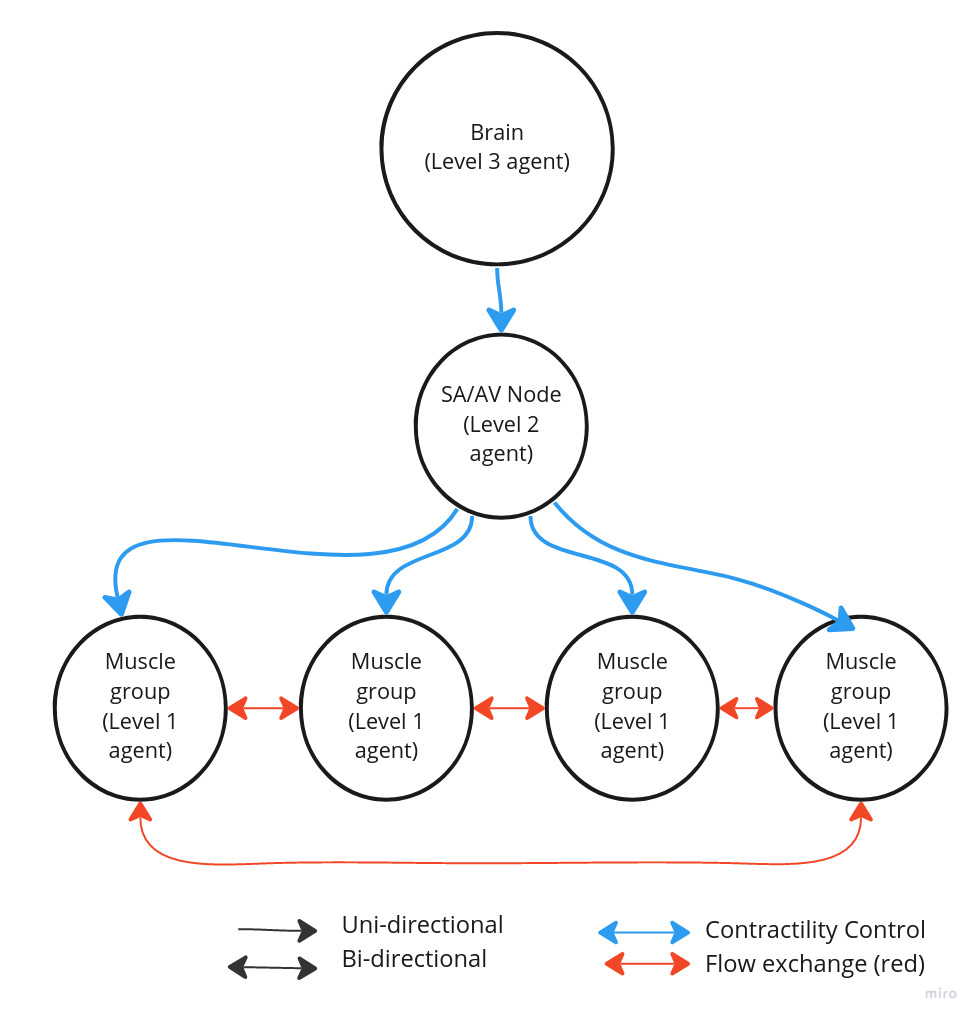
Environment creation as Graph
- Each MAS agent is represented as a vertex v in a weighted directed graph G, where G = (V,E) for v € V.
- A edge e = uv, is a directed edge with weight equal to blood pumped by vertex u to v.
- Each edge has a capacity c_e.
- Flow (f_uv) through each edge uv is flow from u to v, such that f ≤ c_e.
Agent
- has 2 types of properties: Mutable and immutable properties.
- Immutable properties cannot be changed and are inherent constraints of the agents. Like – Parent, child, inherent rhythm, max and min lumen size
- Mutable rhythm: can be changed on external or internal stimuli: eg lumen size, contractility
- Agent characteristics: Agent_type, Parent vertex, Child vertex, inherent_rhythm , current_ryhythm , curr_lumen_size , max_lumen_size , min_lumen_size , efficiency , max_capacity
Edge:
- Weight of edge represents maximum capacity of the edge. This is a dynamic quantity and depends on the pumping ability/capacity of parent vertex.
- It is represented as Capacity = Flow(input_lumen_size , output_lumen_size) = using Reynold’s formula
- curr_capacity(u,v) = capacity(u.curr_lumen_size, v.curr_lumen_size)
- max_capacity(u,v) = capacity(u.max_lumen_size, v.max_lumen_size)
Solution
Build a MAS to show that optimal flow is achieved when agents coordinate for contraction.
Initial state:
We begin with random initialization, such that rhythm of each agent is randomly assigned from their range of max and min contractibility.
Problem framing:
We will divide this problem into two sub-problems:
Max Flow problem in a weighted graph – Ford Fulkerson algorithm for Max Flow, where weights change with every time step. This gives us max flow at any point based on current state of all the agents.
Second is optimization problem where we try to increase each agent’s capacity (i.e. weight of edges) such that loss is minimized. Using Gradient descent method
Loss function for optimization:
- For optimization, Loss = MSE (possible_flow , actual_flow after MaxFlow algorithm) (for single agent as well as overall loss)
